Modernize your Java Spring Boot application with Azure Database for MySQL
This blog post is co-authored by Parikshit Savjani, Senior Program Manager, Azure OSS Database service.
Spring is a well-known Java-based framework for building web and enterprise applications addressing the modern business needs. One of the advantages of using the Spring Boot framework is that it simplifies the data access from relational and NoSQL data stores. Spring Boot framework with MySQL Database backend is one of the established patterns to meet the online transactional processing needs of business applications. The modern business applications are built and deployed on cloud native microservice platforms like Azure Kubernetes service (AKS) moving away from traditional monolithic design to meet the elastic scale and portability needs. The databases on the other hand have more stateful requirements with atomicity, consistency, durability, resiliency, and zero data loss across failures. It is therefore more suited to run databases outside of Kubernetes environment on managed database services like Azure Database for MySQL service which meets these requirements.
Developers and customers can easily build and deploy their Java Spring Boot microservices application in Azure platform thereby improving developer productivity and enabling businesses to achieve more with the following solutions.
- Azure DevOps, a developer platform to build automated and robust CI/CD pipelines.
- Azure Kubernetes Service, a managed Kubernetes platform.
- Azure Container Instance, a serverless container platform for running containerized solutions on Azure.
- Azure Database for MySQL, a fully managed, enterprise ready community MySQL database as a service, .
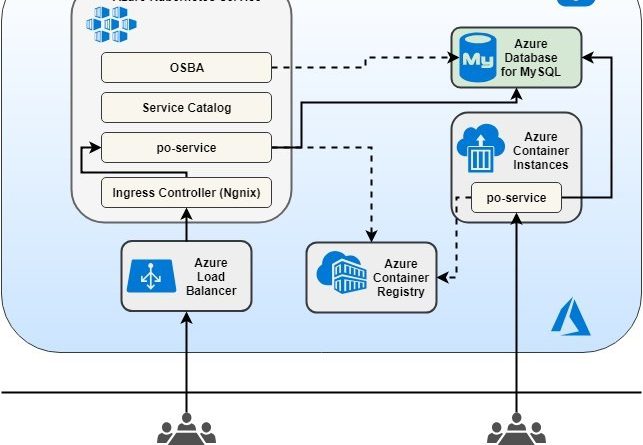
The following is a functional architecture sample of a Java Spring Boot microservices application called po-service on Azure. This Spring Boot application demonstrates how to build and deploy a purchase order microservice as a containerized application on Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS). The deployed microservice supports all CRUD operations on purchase orders.
To enable and integrate the microservices application running on Azure Kubernetes services with the database running on Azure Database for MySQL service, developers can utilize and leverage Open Service Broker for Azure together with Kubernetes Service Catalog.
We have published detailed step-by-step instructions to build and deploy the above architecture in our GitHub repository. The overall goal of this step-by-step guide is:
- To demonstrate the use of Open Service Broker for Azure to provision, deploy, and integrate Azure Database for MySQL from Azure Kubernetes Service seamlessly using the DevOps pipeline.
- To demonstrate the use of Helm (CLI) for deploying containerized applications on Kubernetes (AKS). Helm is a package manager for Kubernetes and is a part of CNCF. Helm is used for managing Kubernetes packages called Charts.
- To demonstrate how to secure a microservice (REST API) end-point using SSL/TLS (HTTPS transport) and expose it through the Ingress Controller addon on AKS.
- To demonstrate the serverless container solution by deploying the microservice on Azure Container Instances (ACI).
Next steps
Get started with building and deploying your microservices application with managed database services on Azure today. You can leverage the instructions from the GitHub repository to build and deploy any microservices application on Azure Kubernetes service or Azure Container Instances (ACI). You can do this with databases running on fully managed Azure database services (PaaS) with end-to-end CI/CD platform running on Azure DevOps. We encourage the developer community to reuse it and raise issues or contribute back by sending a pull request.
Please continue to provide feedback on the features and functionality that you want to see next. If you need any help or have questions, please check out the Azure Database for MySQL documentation. Follow us on Twitter @AzureDBMySQL for the latest news and announcements.
Source: Azure Blog Feed